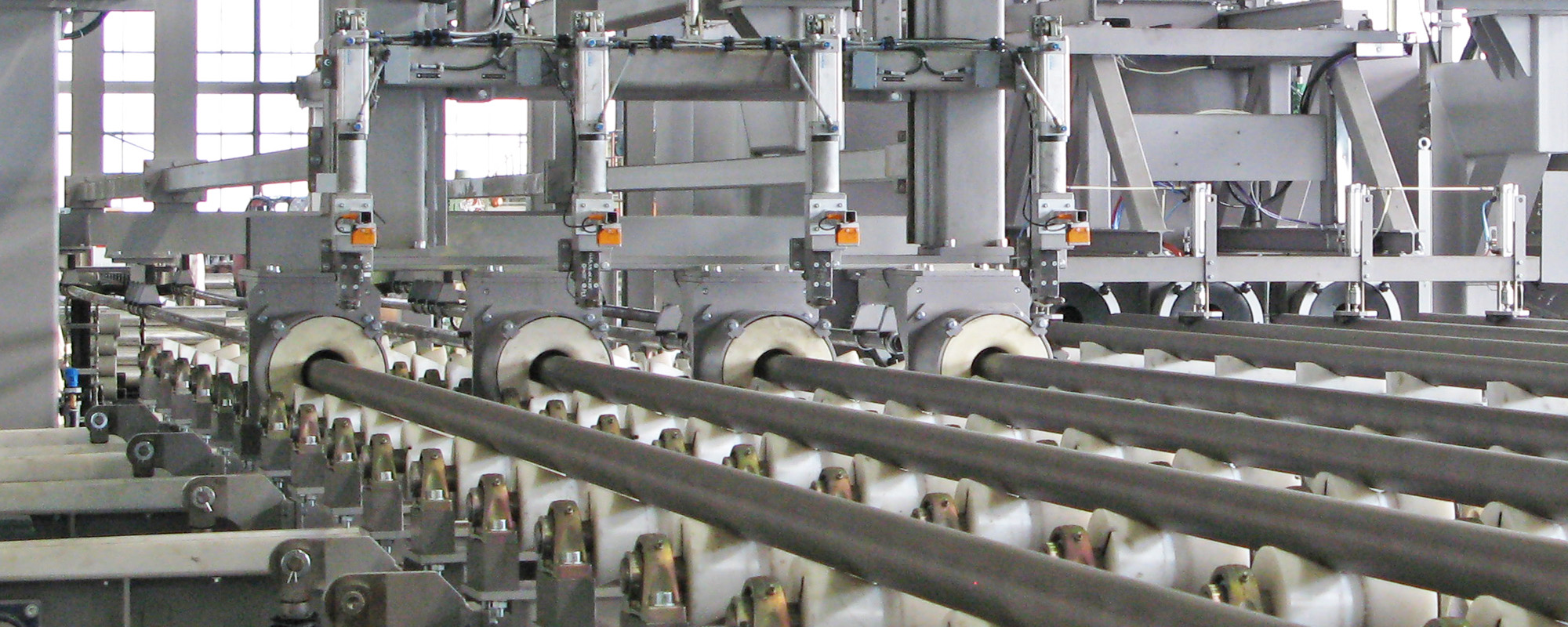
Tube Blast Machines
In contrast to other hollow bodies, tubes can be blasted horizontally because the abrasive or compressed air can escape from the other end. The tube blasting process comprises the actual blasting process and the subsequent air purging with compressed air. To prevent isolated abrasive grains from penetrating again, pure air supplied via a bypass is used instead of blasting air for air purging.
Tubes with small diameters are blasted using the blast-through method, tubes with large diameters using the lance method:
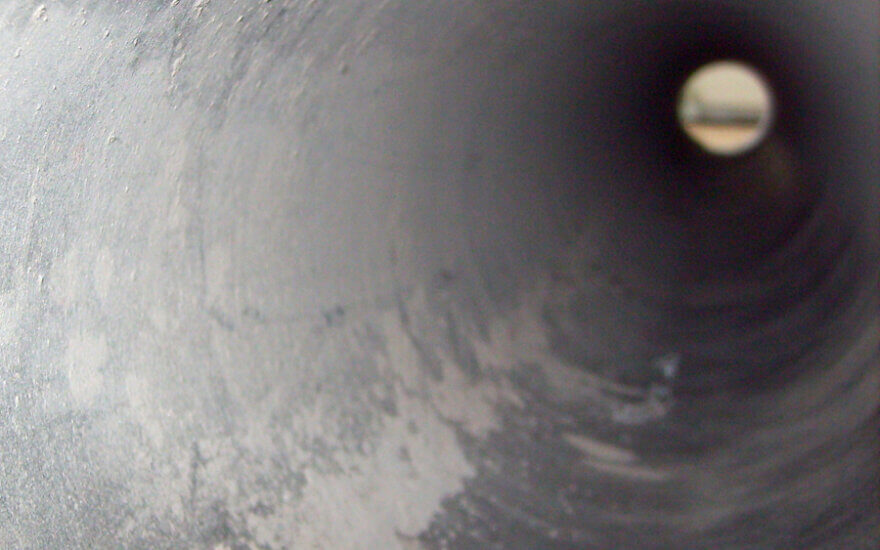

Untreated tube
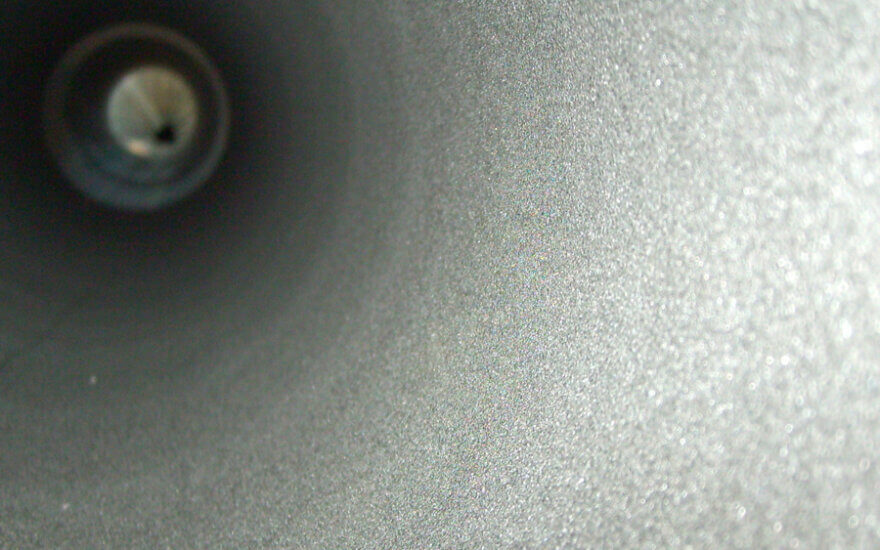

Blasted tube
Application examples
Blast-through method
In the blast-through method, tubes are blasted solely by the reflection of the abrasive from the inner wall of the tube. In the simplest case, the blasting nozzle and suction hose are connected to the two opposite ends of the pipe for this. If processing multiple pipes next to one another in parallel, the abrasive is collected in a collecting cabinet and transported from there back to the blasting system.
Internal blasting of titanium tubes (exiting abrasive)
Internal blasting of titanium tubes (exiting abrasive)
Precision tubes
Targeted material abrasion & defect removal
Precision tubes are customized to an exact dimension with abrasive blasting. Thanks to their closed blasting abrasive circuit, Problast® Machines are ideally suitable for blasting the inside of tubes:

2×2-station blasting system with Problast closed-circuit Machine

Nozzle and tube docking device
The pneumatically moving docking devices are provided with special seals. Dust-free tube blasting is enabled in conjunction with the vacuum generated by the Problast closed-circuit machine.
Tube blasting system for removal of defects from the drawing process
Stainless steel tubes: Removing a layer
Blasting as a substitute process for chemical abrasion by pickling:

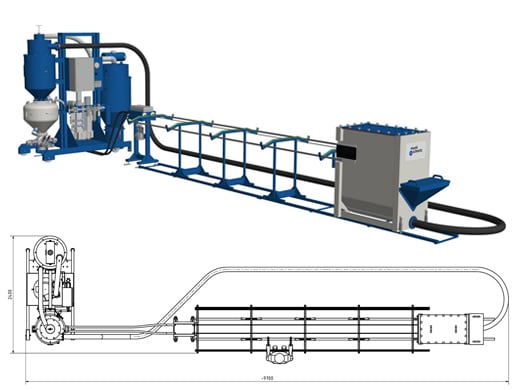
2×4-station blasting system with variable blast nozzle positioning for 6 to 15 m long tubes

Combined feed and blasting unit with 4 nozzle heads
Tubes that have to be blasted from both sides are moved with feed arbours in a longitudinal direction.
Therafter, the blasting heads are jointly docked and the blasting process can begin.
Internal blast cleaning of stainless steel tubes
Video clip
Internal blast cleaning of stainless steel tubes
Copper tubes: Reducing the carbon content
Copper tube blasting systems are usually used for blasting semi-hard tubes for the installation area. The carbon content on the surface of the tubes is reduced by the blasting process. At the same time, formation of the malachite layer, which provides protection from corrosion, is especially promoted by roughening the surface. Chilled cast iron, stainless steel grit or aluminium oxide are optionally used as blasting abrasives.

12-station blasting system with tube singling

Abrasive collecting cabinet
The blasting nozzles are designed so that the pipes are blasted right from the start. The escaping abrasive is collected in a collecting cabinet located opposite and returned to the blasting process after treatment (cleaning).
Internal blast cleaning of copper tubes
Lance blasting method
In case of larger tube diameters, the blasting nozzles mounted at the end of a lance are moved into the tube. The tubes are optionally blasted by a circular blast nozzle or by an angled blast nozzle with simultaneous tube rotation.
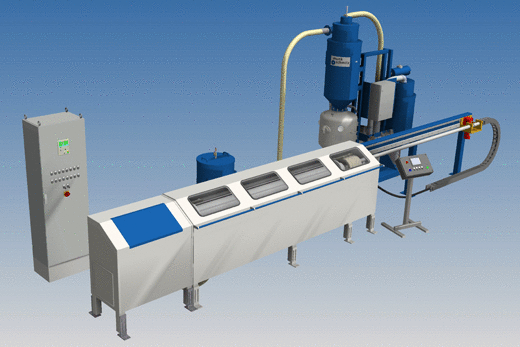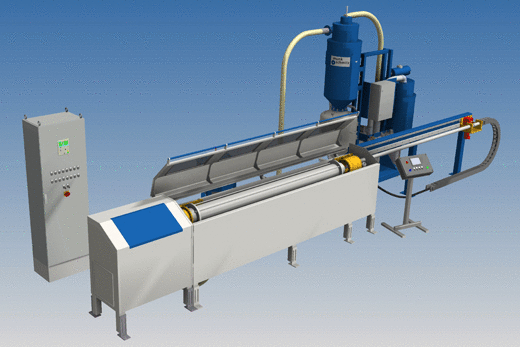
Lance blasting machine with single cabinet and tube rotation (option)
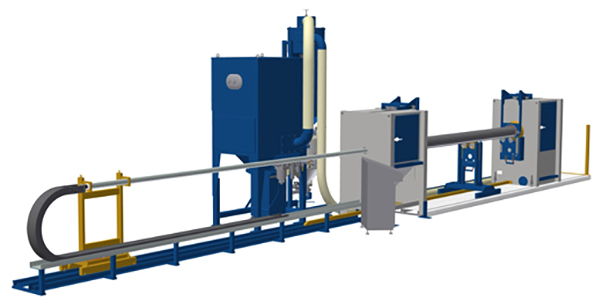
Lance blasting machine with two cabinets and tube rotation (option)

Circular bast nozzle

Angular blast nozzle(s)
Application Examples
Oil transport tubes: Decontamination
The radioactive sludge depositing on the tube walls during the oil transport is removed by abrasive air blasting. The dust is discharged into special disposal vessels.

1-station blasting system with tube rotation

Rotation device and abrasive collectin cabin
The tube end is positioned in an abrasive collecting cabin. The blasting lance is then moved into the tube and – whilst reversing – blasting and air-purging the tube.
Steel tubes: Scale removal after heat treatment
Due to large tube diameters a nozzle head with rotating blast nozzles is used here.

1-station blasting system with rotating nozzle head
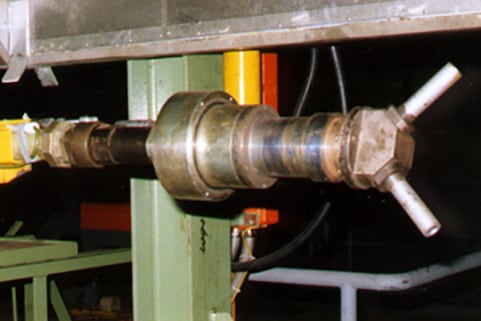
Rotating nozzle head mounted onto blast lance
The nozzle head is equipped with two large blasting nozzles. The rotation is generated via a pneumatic drive.
Combined internal and external blasting
Tubes are frequently blasted internally and externally. If the tube lengths are small, a combination of internal and external blasting can be performed simultaneously with airblasting machines. With long tubes, however, external blasting is performed with dedicated wheelblasting machines.

Application examples
Centrifugal casting moulds: periodical cleaning
Casting moulds need to be cleaned periodically. With this machine they are blastcleaned internally and externally in one operation.
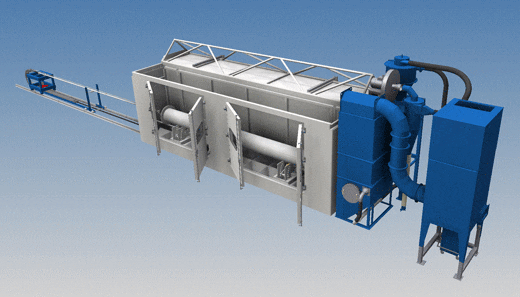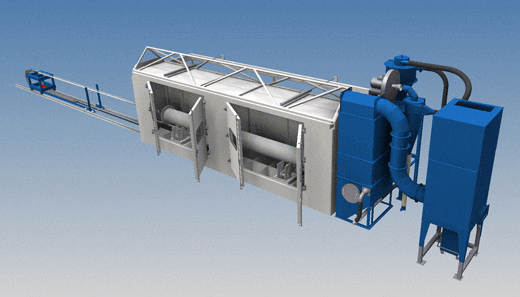
Blasting facility for centrifugal casting moulds featuring a retractable roof

Blasting facility (external view)

External blasting

Internal blasting
Steel tubes: Scale removal
Internal descaling of tubes usually goes long with external shotblasting by wheelblast machines. In this case is advisable to blast the inside after the outside, because internal blasting also removes remainders of abrasive that has been carried into the tubes by external blasting.
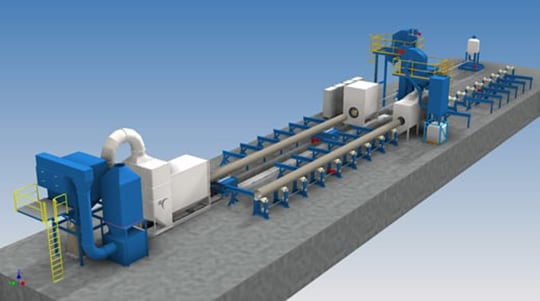
Combined facility for internal and external blast cleaning
Aluminium tubes: Roughening before bonding
Aluminium tubes are roughened with aluminium oxide before internal foaming and external bonding.

Combined internal and external blasting system

Internal and external blasting nozzles
The tubes can optionally be blasted internally and externally in parallel or in succession. The tube is rotated during the blasting process and subsequent air-purging.
Dust-free internal blasting with blast gun
Starting with an internal diameter of approx. 250 mm tubes can alternatively be blasted dust-free by means of a blast gun in combination with a Problast® closed-circuit machine. The otherwise necessary abrasive collection cabin as well as the back transport of the abrasive are no more required.

Dust-free internal blasting with Problast closed-circuit machine




